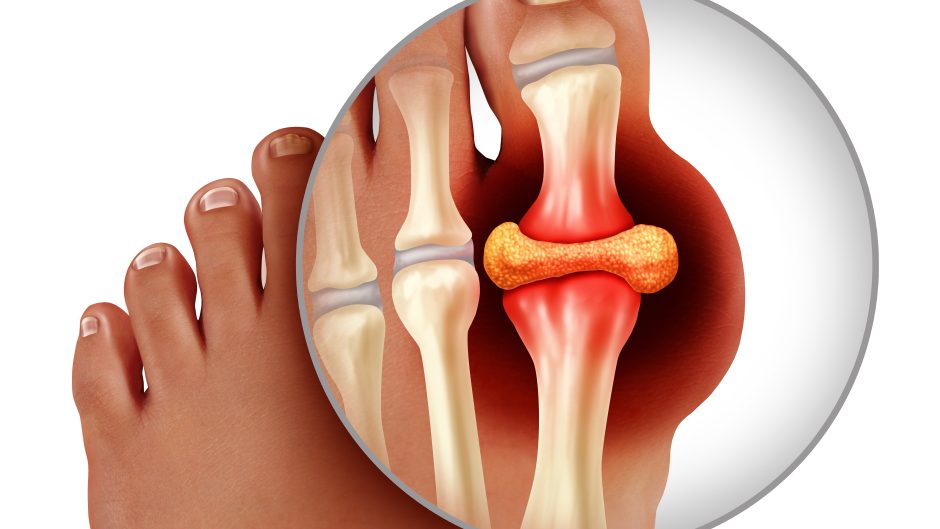
Gout is a type of arthritis and occurs when uric acid accumulates in the blood and causes inflammation in the joints. Sometimes, these crystals are deposited in the kidneys, causing Nephritic Colic or alterations in their function.
In this Channel you can learn more about Gout: Gout Home Remedy
Pathophysiology of Gout
The greater the degree and duration of hyperuricemia, the greater the probability of developing gout. The causes that produce an elevation of uric acid concentration are:
- Decreased renal (most common) or gastrointestinal excretion.
- Increased production (rare)
- Increased purine intake (usually in combination with decreased excretion).
- It is not known why some people with high serum uric acid (urate) concentration develop acute exacerbations of gout and others do not.
Decreased renal excretion: this is the most common cause of hyperuricemia. It can be hereditary (e.g., due to variations in the efficiency of the uric acid transporter), and is also observed in patients receiving diuretics and in those with diseases that decrease glomerular filtration. Ethanol increases purine catabolism in the liver and the formation of lactic acid, which blocks urate secretion in the renal tubules and can also stimulate hepatic urate synthesis. Lead poisoning and cyclosporine, in the higher doses used for transplant patients, alter renal tubular function, with urate retention.
If you don’t know the symptoms of gout you can learn more about it here: Gout Symptoms
Increased urate production may be due to increased nucleoprotein turnover in hematologic diseases (e.g., lymphoma, leukemia, hemolytic anemia) and in those with increased rates of cell proliferation and cell death (e.g., psoriasis, cytotoxic cancer treatment, radiation therapy). Increased urate production may also manifest as a primary hereditary abnormality or with obesity, as urate production correlates with body surface area. In most cases, the cause of urate overproduction is unknown, although it is rarely attributed to enzymatic abnormalities; one possible cause is hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is the complete deficiency) or overactivity of phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase.
Increased intake: increased intake of purine-rich foods (e.g., liver, kidneys, anchovies, asparagus, broth, herring, meat sauce and broth, mushrooms, mussels, sardines, sweetbreads) may contribute to hyperuricemia. Beer, including non-alcoholic beer, is particularly rich in guanosine, a purine nucleoside. However, a strict low-purine diet decreases serum urate concentration by only 1 mg/dL (0.1 mmol/L) and therefore is rarely sufficient therapy for patients with gout.
Here you can purchase the best natural supplement against Gout: Gout Treatment
Urate precipitates as acicular monosodium urate crystals that form extracellular deposits in avascular tissues (e.g., cartilage) or in relatively avascular tissues (e.g., tendons, tendon sheaths, ligaments, bursa walls) and in the skin around joints and colder distal tissues (e.g., ears, finger pads). In cases of prolonged severe hyperuricemia, monosodium urate crystals may be deposited in large central joints and in the parenchyma of organs such as the kidney.
At the acidic pH of urine, urate precipitates readily as small, plaque-like or diamond-shaped uric acid crystals that may aggregate to form grit or stones, which can obstruct the flow of urine. Tophi are aggregates of monosodium urate crystals that develop in joints and skin tissues. They are usually enclosed in a granulomatous fibrous matrix, which prevents them from causing acute inflammation.
Acute gouty arthritis can be triggered by trauma, illness (e.g., pneumonia or other infection), surgery, use of thiazide diuretics or drugs with hypouricemic effects (e.g., allopurinol, febuxostat, probenecid, nitroglycerin), or by abuse of purine-rich foods or alcohol. Acute exacerbations are usually precipitated by a sharp rise or, more frequently, a sharp fall in serum urate levels. The reason why acute flares follow some of these precipitating conditions is unknown. Tophi in and around joints can limit movement and cause deformities, called chronic tophaceous gouty arthritis. Gout increases the risk of developing secondary osteoarthritis.
There are many home remedies that help prevent gout, here you can learn more about these remedies: Home Remedies For Gout